Range Extenders in Electric Vehicles: Range Without Regrets
- Wolfgang A. Haggenmüller

- Jul 8, 2025
- 8 min read

The return of a technology believed dead
For a long time, it was considered a transitional technology – a technical crutch on the way to an all-electric future: the range extender. But while many had already written him off, he is suddenly celebrating a remarkable comeback. At Auto Shanghai 2025, manufacturers such as Leapmotor, Li Auto and Nissan proudly presented their new models – equipped with the once discredited range extension. And suddenly the technology, which already caused a sensation with the BMW i3 REx 2013, is highly topical again. So why is the range extender experiencing a renaissance right now? The answer lies in a mix of market reality, infrastructure deficits, political framework conditions – and the pragmatic insight that battery-electric mobility cannot work everywhere and immediately. What initially looks like a step backwards could turn out to be a decisive bridge to a sustainable mobility turnaround.
Review of the Shanghai Auto Show 2025
The 2025 Shanghai Auto Show showcased a remarkable return of range extender technology. Chinese manufacturers such as Leapmotor presented models such as the C10 with range extender, and international brands such as Volkswagen also announced corresponding developments. This renaissance of the technology, which was once considered a temporary solution, shows its renewed relevance in the context of electric mobility.
History and first applications
The idea of the range extender, i.e. an additional unit for extending the range of electric vehicles, is not new. As early as the early 2010s, vehicles such as the Opel Ampera and the BMW i3 were equipped with this technology. The BMW i3, introduced in 2013, offered an optional 647cc twin-cylinder petrol engine as a range extender that drove a generator to charge the battery while driving.
In 2011, Prof. Dr. Ferdinand Dudenhöffer commented on the range extender in automotiveIT: "The range extender is two years ahead of the competition. GM and Opel have developed a real USP with the Volt and the identical Opel Ampera." This quote underlines the technological leadership of GM and Opel in the field of range extender vehicles at the time.
Technical functionality
A range extender typically works as a serial hybrid drive. A small combustion engine drives a generator that generates electrical energy. This energy is either transmitted directly to the electric motor or stored in the battery. Unlike parallel hybrid systems, there is no mechanical connection between the internal combustion engine and the drive wheels, which reduces weight and complexity.

A range extender is usually designed as a serial hybrid: The combustion engine does not drive a wheel directly, but generates electricity via a generator. This charges the battery or supplies the electric motor directly – the actual drive remains purely electric. This eliminates the need for a complex mechanical drive train and transmission. Compact petrol engines with a displacement of 1.0–1.5 litres are typical, which run efficiently in a constant speed range. Examples: A 2-cylinder motorcycle engine was used in the BMW i3 REX, while Mazda uses a particularly space-saving Wankel engine in the MX-30 R-EV. Alternative concepts such as microturbines are also being tested. The combustion engine starts automatically when the battery is almost empty. In some models, the generator can also be switched on manually, for example to buffer the battery before longer journeys. The driving experience always remains electric: quiet, direct and without noticeable shifting. Alternative energy sources such as fuel cells or gas turbines are theoretically possible, but proven combustion engine solutions currently dominate – for reasons of simplicity and availability.

Reasons for the temporary failure
Despite their advantages, range extenders have not been able to establish themselves permanently in the past. The reasons for this included the increasing improvement of battery technology, which led to longer ranges, and the desire for completely emission-free vehicles. In addition, vehicles with range extenders were not recognized as pure electric vehicles in some markets, which led to disadvantages in terms of subsidies.
Current relevance and future developments
Recently, range extender technology is experiencing a revival, especially in Asia. Vehicles such as the Nissan Qashqai e-Power use an internal combustion engine exclusively to generate electricity, while the drive is purely electric. European manufacturers such as Volkswagen are also looking into reintroducing this technology to facilitate the transition to electric mobility.ecomento.de+2Blick+2ingenieur.de+2ingenieur.de+1Elektroauto-News.net+1Automobilwoche
The rise of REEVs is part of a broader trend in the automotive industry that focuses on innovative solutions to meet consumer demands and regulatory requirements. As a bridge between traditional internal combustion engines (ICE) and battery electric vehicles (BEVs), REEVs offer more flexibility and range.
Pros and Cons
Benefits of Range Extender Vehicles
Less range anxiety: Long journeys are possible without a charging break – simply refuel and continue driving. This is particularly helpful in regions with poor charging infrastructure.
Smaller battery, lower costs: The additional combustion engine can make the battery smaller – this saves weight, resources and lowers the price (e.g. in China about 4000 € cheaper than pure electric cars).
E-driving experience suitable for everyday use: In short-distance operation, the vehicle drives purely electrically, quietly and emission-free. The combustion engine only runs in the background when needed.
Flexible use: Charging at the socket is possible, but not absolutely necessary. Ideal for users who cannot always charge reliably.
Efficient combustion engine operation: The range extender runs in the optimal range, which enables high efficiencies (up to 50%) and low fuel consumption(e.g. Mazda with 1.0 L/100 km WLTP). Less wear and maintenance due to low use.
Disadvantages of Range Extender Vehicles
Greater complexity and maintenance: Two drive systems increase weight, costs and maintenance. The combustion engine must be operated and maintained regularly.
Not completely emission-free: CO₂ and exhaust gases are produced in generator operation – environmental zones or subsidies could be restricted.
Energy losses: The detour via power generation reduces the overall efficiency. On long distances, consumption is higher than with pure combustion engines.
More weight, less space: Additional technology takes up space and makes the vehicle heavier, which can reduce range and utility.
Limited future-proofing: Advances in all-electric cars (range, cost) and possible legislative changes could make the range extender superfluous. The resale value could fall in the long term.
Legal and political framework
In Germany, the Electric Mobility Act (EmoG) was introduced to promote the use of electric vehicles. However, vehicles with range extenders were not always classified as eligible, which reduced their attractiveness. Political parties such as the CDU/CSU and SPD are currently discussing new incentives for electric vehicles, which could also have an impact on the acceptance of range extender models.
Current and planned vehicle models
In addition to the aforementioned Nissan Qashqai e-Power, manufacturers such as Leapmotor and Hyundai are planning to introduce new models with range extenders. Hyundai, for example, is working on a small combustion engine that could increase the range of electric cars to up to 1000 kilometers.
The Li Auto L9 is a modern electric SUV with a range extender from China – an example of the growing number of such vehicles worldwide. Manufacturers relied on this technology early on to reduce range anxiety in electric cars. Here is an overview of some models:
· Opel Ampera / Chevrolet Volt (2011): Early pioneers with an electric range of around 40–80 km, after which a 1.4-liter gasoline engine provides around 500 km of additional range.
· BMW i3 REX (2013): Compact electric car with 647 cc two-cylinder generator. With a 9-litre tank, around 120–150 km of additional range. Innovative thanks to CFRP body and counter-rotating doors.
· Polestar 1 (2020): Powerful plug-in hybrid with 34 kWh battery for 124 km electric. Combustion engine drives the front wheels, electric motors the rear wheels – a technology carrier in small series.
· Li Auto L9 (since 2022): Chinese luxury SUV with 44.5 kWh battery (200 km electric) and 1.5-liter generator. Total range approx. 1200 km, powerful equipment and 408 hp system output.
· Mazda MX-30 R-EV (2023): Compact crossover with Wankel engine as a range extender. Electric range: 85 km, total over 600 km. The combustion engine only charges, never drives directly.
· Leapmotor C10 REEV (from 2025): New Chinese crossover with a total range of over 950 km. Combination of electric drive and generator eliminates range anxiety.
· Nissan e-Power relies on serial hybrids without a charging port – a special form of the range extender. The diversity shows the flexible application of this technology worldwide.
· BMW Top It is currently reported that the Bavarian manufacturer is working together with ZF on an EREV drive, which is already being tested in an iX5. The drive is to be used in the iX5 REx and could be launched as early as 2026.
· A few months ago, Volkswagen announced plans to integrate range extenders into current models. Speculation ranges from the ID.4 to the ID.7.
S&P Global Mobility predicts that global production of light REEV vehicles will reach 1.238 million units by the end of 2024, the majority of which will be built in Greater China for this regional market.
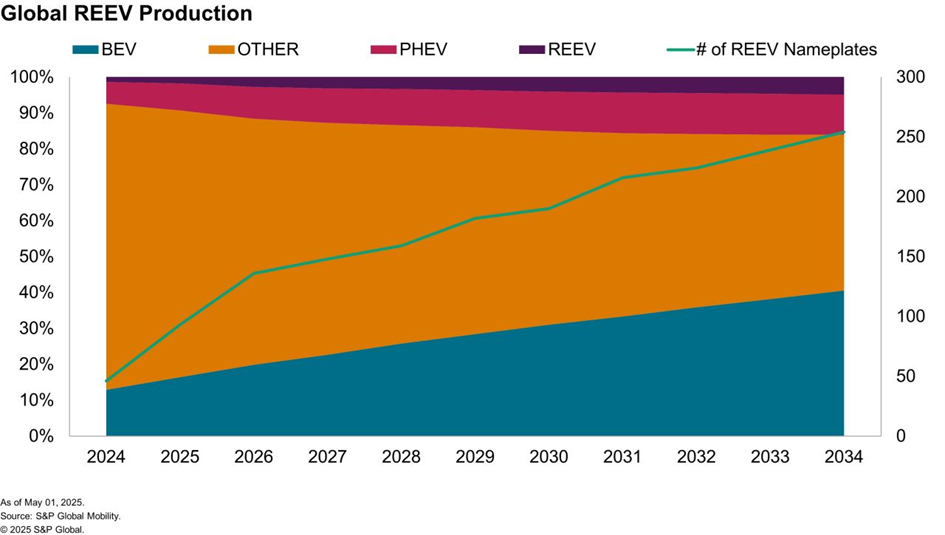
Regional market developments
The evolution of the range extender vehicle (REEVs) market varies significantly globally, influenced by regional differences in infrastructure, politics, consumer preferences, and technological advancements. The following is an overview of developments in Europe, Asia (with a focus on China and Japan) and the US, including the major players in the automotive industry and range extender manufacturers.
Europe
In Europe, the market for range extender vehicles is currently limited, due to several factors:
Strict emissions regulations: The EU has set ambitious targets to reduce CO₂ emissions, which puts the focus on pure electric vehicles (BEVs).
Subsidy policy: Subsidies and tax benefits are mainly focused on BEVs, while REEVs often do not benefit to the same extent.
Infrastructure: The expansion of the charging infrastructure in many European countries reduces the need for range extenders.
Despite this, there are signs of growing interest in REEVs, especially in countries with less developed charging infrastructure or in rural areas.
China
China is currently the world's largest market for electric vehicles and is showing strong growth in the field of REEVs:
Government support: The Chinese government promotes "New Energy Vehicles" (NEVs), which include REEVs, through subsidies and policies.
Market demand: Chinese consumers are showing interest in vehicles with a longer range, which is increasing the demand for REEVs.
Technological innovation: Chinese manufacturers are investing in advanced battery technologies and range extender systems to increase competitiveness.
One example is Li Auto, which specializes in REEVs and produced over 500,000 vehicles in 2024. Wikipedia
Japan
In Japan, manufacturers such as Nissan are relying on hybrid technologies such as the e-Power system, which uses a gasoline engine to generate electricity while the drive is purely electric. AP News
United States
In the US, interest in REEVs is moderate, influenced by:
Market preferences: U.S. consumers often prefer larger, longer-range vehicles, making REEVs attractive.
Political uncertainty: Changing political conditions and subsidy programs influence investments in REEV technologies.
Manufacturers such as Ford and Mazda are developing REEVs to serve the US market. TopElectricSUV
Key players in the automotive industry and range extender manufacturers
Automobile manufacturer
Li Auto: Chinese manufacturer specializing in REEVs.
Nissan: Japanese manufacturer with the e-Power system.
Mazda: Develops REEVs with Wankel engine technology.
Ford: Plans to introduce REEVs in the USA.
Volkswagen: Researches REEV technologies for various markets.
Range Extender System Manufacturer
MAHLE Powertrain: Develops serial hybrid drives for REEVs.
ZF Friedrichshafen: Offers integrated range extender systems. e-hybrid vehicles Tech International
AVL: Conducts research and development in the field of range extenders.
Magna International: Offers components for REEVs.
Expert opinions
According to a study by the German Aerospace Center (DLR), range extenders offer a sensible transitional solution to increase the adoption of electric vehicles, especially in regions with inadequate charging infrastructure.
Result
Range extender technology has found both supporters and critics in the past. However, with current developments and the increasing demand for flexible mobility solutions, it could play an important role in the transition to full electric mobility. The combination of technical development, political incentives and changing user needs speaks for the renewed relevance of this technology. The development of the market for range extender vehicles is strongly influenced by the region. While China plays a leading role, Europe and the US are more restrained, influenced by different political, economic and infrastructural factors. Key players in the automotive industry and range extender manufacturers are adapting their strategies accordingly to meet the specific needs and opportunities in their respective markets.



Comments